
June 2020
Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus (RHDV2)
By Dr. Gregg Hanzlicek
Both domestic and wild rabbits in New Mexico, Texas, and more recently Colorado, have been diagnosed with RHDV2.
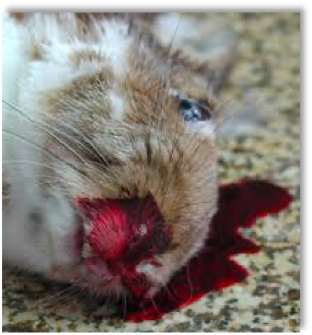
This is an extremely contagious disease with very high mortality.
|
The most common clinical sign is sudden death. This many times involves a large numbers of rabbits within a specific geographical location. Other signs observed may include blood stained nares and some rabbits may go off-feed, be febrile or present with nervous or respiratory signs.
Prevention is almost entirely dependent on biosecurity and sanitation including washing hands while working with rabbits and not sharing housing or equipment with other owners. (There is a vaccine available only in Colorado.)
This virus is not infectious to other animal species, including humans.
This is considered to be a foreign animal disease (FAD); in cases when veterinarians suspect RHDV2, they should contact their State Veterinarian’s Office for assistance in sampling and diagnoses.
Next: Canine Blood Donor Program
Return to Index